Introduction
Achieving strong and consistent adhesion in industrial environments is vital to ensuring product durability, safety, and long-term performance. Failures in bonding can result in expensive recalls, safety hazards, and disruptions to manufacturing efficiency, making it essential to follow proven best practices. Companies like Leech Adhesives provide valuable expertise and in-depth resources to help manufacturers overcome challenges in industrial bonding. Their website, https://leechadhesives.com/, offers insights into adhesive solutions for various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. Understanding adhesion mechanisms and partnering with experienced providers is key to success for production teams aiming to meet demanding industry standards.
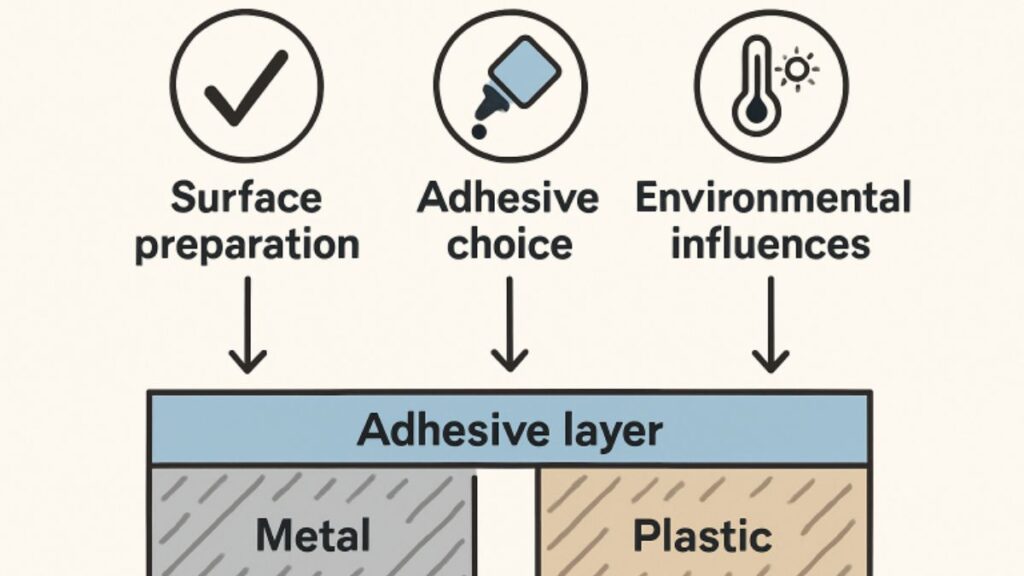
Adopting best practices for industrial adhesion enables manufacturers to address common challenges, optimize bonding processes, and significantly improve product quality. Businesses can outperform competitors in product excellence and efficiency by learning from real-world case studies and leveraging the latest research. The following guide outlines critical approaches to achieving reliable adhesion, from proper surface preparation to ongoing quality control.
Understanding Adhesion Challenges
Tackling adhesion challenges begins with understanding the root causes behind bonding failures. Frequent culprits include inadequate surface treatment, contamination by oils or dust, and mistaken adhesive selection for given substrates. These issues can introduce significant vulnerabilities into final products, leaving them at risk for premature separation, structural compromise, or functional breakdown. Recognizing these issues early in production can prevent defects that might only become visible after the final assembly or during end use, resulting in substantial savings and improved reputation.
Adhesion is influenced by a range of variables, including material compatibility, environmental exposure, and the mechanical stresses experienced by the bond. Temperature, UV light, chemical exposure, and vibration can all contribute to reduced adhesion strength over time. Overlooking any one of these factors can result in compromised bond strength, leading to potential safety hazards or the need for costly repairs. Tailoring the entire adhesive process to the specific demands of the application and substrate is crucial, as it reduces risk and ensures long-term reliability.
Surface Preparation Techniques
Surface preparation is foundational to maximizing adhesion strength. Even high-performing adhesives can fail if the substrate is not optimally prepared. The most effective techniques include:
- Cleaning: Industrial surfaces must be free of contaminants such as oils, greases, and particulate matter. Solvent wipes, alkaline cleaners, and ultrasonic baths are commonly used to ensure pristine surfaces. Choosing the right cleaning agent depends on the type of substrate and the contaminants present, requiring knowledge of chemical compatibility to prevent inadvertent damage.
- Mechanical Abrasion: Increasing the surface roughness by sanding, brushing, or blasting helps create mechanical “locks” with which adhesives can bond. This process is vital for metals and rigid plastics, as micro-level texture enables the adhesive to form more robust connections, thereby improving joint durability under stress.
- Chemical Treatments: Chemical etching, priming, or plasma treatments modify surface energy and enhance adhesive wetting and penetration, especially on low-energy substrates like polyethylene or PTFE. These advanced techniques alter the surface chemistry, promoting a better molecular interaction between the adhesive and the substrate.
Timing and environmental controls during preparation also matter—humidity and temperature can influence cleaning outcomes and the effectiveness of treatments. For in-depth information on the science and importance of surface preparation, reputable sources such as Assembly Magazine offer additional context and best-practice recommendations.
Choosing the Right Adhesive
The correct adhesive must be selected based on the substrate and the operational context. Key considerations include chemical compatibility, resistance to temperature extremes, humidity levels, and the anticipated load on the joint. The operating environment—indoors, outdoors, extreme climates—also influences the type of adhesive. For example, epoxies may provide exceptional strength for metals, while polyurethanes are favored for flexible or vibrational bonds. Acrylic adhesives may be specified for fast-setting applications, while silicones are suited for high heat and vibration.
Manufacturers often work closely with adhesive suppliers to evaluate specific product performance data, application techniques, cure times, and safety considerations. Testing for peel strength, impact resistance, and long-term stability is essential when narrowing product choices. This partnership allows for tailored recommendations and testing, helping ensure the chosen adhesive functions optimally under real-world conditions. Seeking professional advice reduces the likelihood of costly mistakes and performance shortfalls.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Sustained performance in industrial adhesion is founded on rigorous quality control protocols. Regularly scheduled testing and monitoring—such as pull-off tests, shear tests, and lap-shear tensile strength measurements—identify inconsistencies before products leave the facility. Quality checks must be consistent at every stage: from incoming material inspection to final product evaluation, creating multiple safety nets that catch flaws before they become customer-facing problems.
Contact angle measurements are frequently used to verify that surfaces are adequately prepared for bonding. Variations in these readings can quickly highlight contamination or improper preparation. Documentation of test results facilitates troubleshooting when problems arise and supports continuous improvement initiatives. Establishing standard operating procedures (SOPs) for adhesive application, curing conditions, and post-cure inspections will boost consistency and confidence in product performance. For broader insights into industrial QC techniques, the Quality Magazine provides extensive testing and assurance protocols resources.
Training and Education
Building a culture of quality relies on thorough training and ongoing education for all personnel involved in adhesive processes. Operators should be familiar not only with application methods and equipment but also with the science behind adhesion and the impact of common issues like contamination or improper mixing. Developing clear, visual work instructions and providing hands-on practice can bridge knowledge gaps and reinforce key concepts.
Programmatic training and regular refreshers—as well as access to manufacturer documentation—significantly reduce the incidence of human error and raise the level of craftsmanship on the production floor. Addressing misconceptions and teaching troubleshooting skills enables a more proactive workforce, capable of maintaining continuous improvement and adapting to evolving product requirements.
Staying Updated with Industry Standards
Adhering to recognized industry standards and best practice guidelines ensures compliance and helps prevent costly errors. Organizations such as the ASTM and ISO frequently update their protocols for adhesive products and application methods. Knowledge of these standards aids in meeting customer expectations and regulatory requirements in diverse sectors like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. Regularly reviewing and integrating these standards into operating procedures helps manufacturers remain competitive and compliant while promoting continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Successful industrial adhesion is achieved by understanding the roots of everyday challenges, adhering to thorough surface preparation standards, selecting the appropriate adhesive, implementing ongoing quality control, and remaining informed about the latest industry requirements. Companies can address variances and adapt as materials and manufacturing paradigms evolve by investing in technology, continuous staff education, and the right partnerships. Leveraging the expertise and support from reputable resources can strengthen adherence outcomes and set the foundation for durable, high-performance products across any industry.